Definition Of Buffer In Biology
Buffers are commonly used in research labs especially in applications involving protein electrophoresis polymerase chain reaction and Western blotting. Buffer capacity is the amount of acid or base that can be added before the pH of a buffer changes.
 Buffers Definition Overview Expii
Buffers Definition Overview Expii
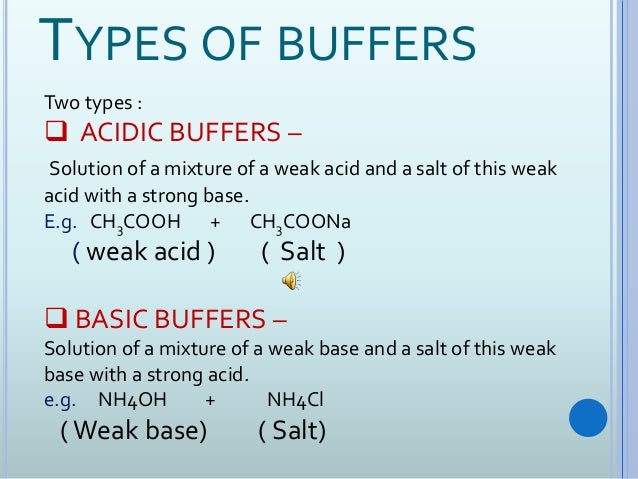
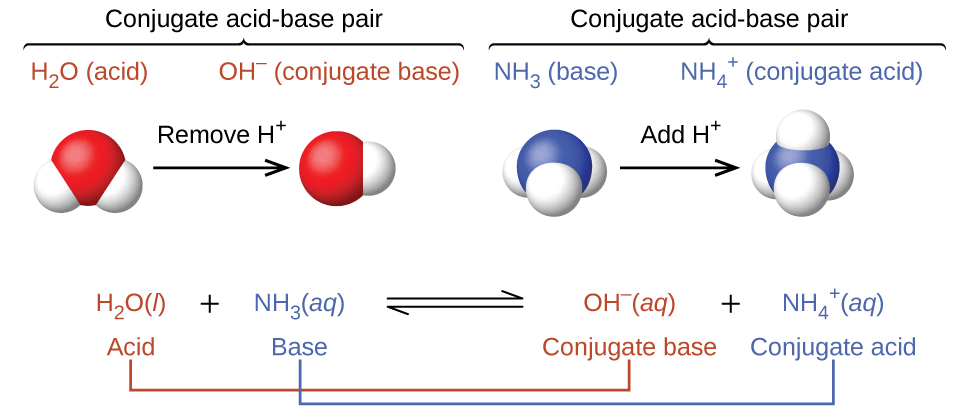
Buffer A buffer solution is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate baseor a weak baseand its conjugate acid.

Definition of buffer in biology. Buffers are used to make solutions of known pH especially for instrument calibration purposes. Chemistry A substance that prevents change in the acidity of a solution when an acid or base is added to the solution or when the solution is diluted. A solution containing either a weak acid and a conjugate base or a weak base and a conjugate acid used to stabilize the pH of a liquid upon dilution.
Cological buffers are protected zones established around sensitive or critical areas such as wildlife breeding or hibernation habitats streams and wetlands to lessen the impacts of human activity and. Buffer a weak acid or base that can react with strong acids or bases to help prevent sharp sudden changes in pH THIS SET IS OFTEN IN FOLDERS WITH. When an acid or alkali has added the pH of the solution changes in the absence of buffers.
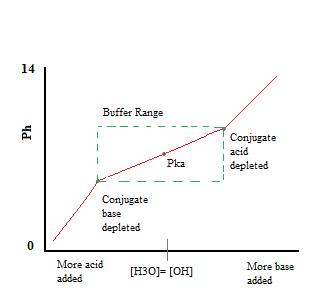
A buffer is an aqueous solution used to keep the pH of a solution nearly constant. A capacity of 1 when 1 mol of acid or alkali is added to 1 litre causes a pH fall or rise of 1 pH unit. It keeps the pH within the proper range.
Carbon dioxide is part of a prominent buffer system in the human body. Biology I - Chapter 2-1. If too much H enters the body bicarbonate will combine with the H to create carbonic acid and limit the decrease in pH.
A buffer solution is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base or vice versa. Buffer a chemical substance which has the capacity to bond to H ions removing them from solution when their concentration begins to rise and releasing H ions when their concentration begins to fall. Biological buffers are organic substances that maintain a constant pH over a given range by neutralizing the effects of hydrogen ions.
Sample Preparation To carry out Western blot analysis you first need a tissue sample. 1 chemistry A buffer solution. A substance or mixture of substances as bicarbonates and some proteins in biological fluids that in solution tends to stabilize the hydrogen-ion concentration by neutralizing within limits both acids and bases.
2 biochemistry An ionic compound that when added to a solution neutralizes both acids and bases without significantly changing the original acidity or alkalinity of a solution. A biological buffer is an organic substance that has a neutralizing effect on hydrogen ions. An example of a common buffer is a solution of acetic acid CH 3 COOH and sodium acetate.
Ions are atoms or molecules that have lost or gained one or more electrons. Buffers are used during cell lysis breakdown protein separation protein transfer and blocking phases. In water solution sodium acetate is completely dissociated into sodium Na and acetate CH 3 COO - ions.
Most buffers consist of a weak acid and a weak base. Buffer in chemistry solution usually containing an acid and a base or a salt that tends to maintain a constant hydrogen ion concentration. Buffers are the mixture of weak acids and their salts of strong bases or the mixture of weak bases and their salts of strong acidsBuffers help to maintain a normal pH of the biological systems.
Medical Definition of buffer Entry 1 of 2 1. How to use buffer zone in a sentence. Buffer capacity A measure of the ability of a solution to maintain its pH in the face of the addition of acid or alkali.
In this way a biological buffer helps maintain the body at the correct pH so that biochemical processes continue to run optimally. In this way buffers stabilize the pH of biological solutions and are thus important in maintaining HOMEOSTASIS. Buffers are the mixtures of weak acids and their salts of strong bases or strong acids and their salts of weak bases.
An area designed to separate. A buffer consists of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. Buffer zone definition is - a neutral area separating conflicting forces.
Return to Search Page. For example the bicarbonate buffering system is used to regulate the pH of blood. This buffer system involves carbonic acid H 2 CO 3 and bicarbonate HCO 3 anion.
Buffers that are continuous around the perimeter or along the length of a sensitive habitat. It has the property that the pH of the solution changes very little when a small. In nature there are many systems that use buffering for pH regulation.
Buffer solutions are used as a means of keeping pH at a nearly constant value in a wide variety of chemical applications. Its pH changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it.
 Introduction To Buffers Chemistry Libretexts
Introduction To Buffers Chemistry Libretexts
 Buffer Solution Acidic Buffer Basic Buffer Animation Buffer Solution Electron Configuration Solutions
Buffer Solution Acidic Buffer Basic Buffer Animation Buffer Solution Electron Configuration Solutions
 Buffer Solution Preparation Of Buffer Solution Acidic Basic Buffer Buffer Action Buffer Solution Solutions Electron Configuration
Buffer Solution Preparation Of Buffer Solution Acidic Basic Buffer Buffer Action Buffer Solution Solutions Electron Configuration
 Pin By Arman Afshar On Data Molecular Biology Biology Teaching Biology
Pin By Arman Afshar On Data Molecular Biology Biology Teaching Biology
 Why Isotopes Are Unstable Chemistry Basics Chemistry Science Student
Why Isotopes Are Unstable Chemistry Basics Chemistry Science Student
 This Video Is First Part Of Uv Spectroscopy It Covers Electromagnetic Spectrum Beer La Teaching Chemistry Electromagnetic Spectrum Medical Laboratory Science
This Video Is First Part Of Uv Spectroscopy It Covers Electromagnetic Spectrum Beer La Teaching Chemistry Electromagnetic Spectrum Medical Laboratory Science
 Digital Kemistry Best Chemistry Animated Blogs What Is Valency In Chemistry Definition Example 11th Chemistry Chemistry Biochemistry
Digital Kemistry Best Chemistry Animated Blogs What Is Valency In Chemistry Definition Example 11th Chemistry Chemistry Biochemistry
 Buffer Buffering Capacity Properties Of Good Buffer And Role Of Buffer In Vitro And In Vivo Online Biology Notes
Buffer Buffering Capacity Properties Of Good Buffer And Role Of Buffer In Vitro And In Vivo Online Biology Notes
 Lec 9 Level 4 De Biological Buffer
Lec 9 Level 4 De Biological Buffer
 Pin De Biology 4u En Simple Biology Videos
Pin De Biology 4u En Simple Biology Videos
 Buffer Solution Preparation Of Buffer Solution Acidic Basic Buffer Buffer Action Buffer Solution Electron Configuration Solutions
Buffer Solution Preparation Of Buffer Solution Acidic Basic Buffer Buffer Action Buffer Solution Electron Configuration Solutions
 Common Ion Effect Buffer Solution And Solubility Product Buffer Solution Solubility Solutions
Common Ion Effect Buffer Solution And Solubility Product Buffer Solution Solubility Solutions
 Genetic Testing Hopes Biology Labs Biology Classroom Biochemistry
Genetic Testing Hopes Biology Labs Biology Classroom Biochemistry
 Common Ion Effect Chemistry Digital Common
Common Ion Effect Chemistry Digital Common