Buffer Solution Definition Biology
You can explore more about buffer solutions here. What is Buffer in Biology.
 Buffer Solution Preparation Of Buffer Solution Acidic Basic Buffer Buffer Action Buffer Solution Solutions Electron Configuration
Buffer Solution Preparation Of Buffer Solution Acidic Basic Buffer Buffer Action Buffer Solution Solutions Electron Configuration
Furthermore it consists of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base or vice-versa.

Buffer solution definition biology. Ions are atoms or molecules that have lost or gained one or more electrons. A solution containing either a weak acid and a conjugate base or a weak base and a conjugate acid used to stabilize the pH of a liquid upon dilution. The osmolarity and ion concentrations of the solutions match those of the human body isotonic.
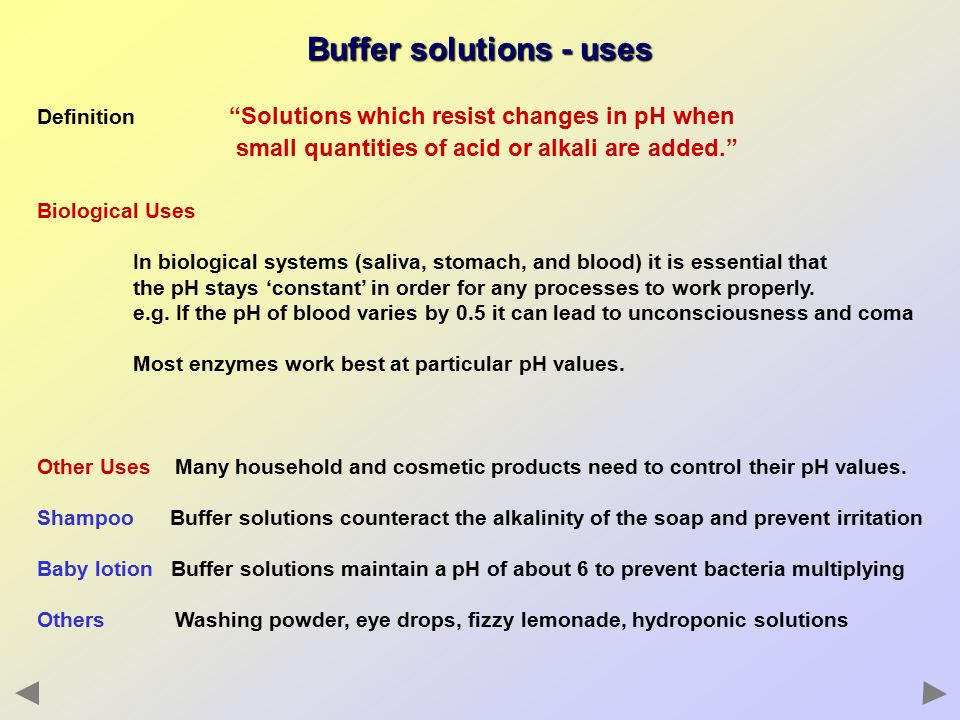
A buffer solution more precisely pH buffer or hydrogen ion buffer is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base or vice versa. The buffer helps to maintain a constant pH. In this way a biological buffer helps maintain the body at the correct pH so that biochemical processes continue to run optimally.
Buffers are solutions that resist a change in pH on dilution or on addition of small amounts of acids or alkali. A buffer solution is one that resists a change in pH on the addition of acid H or base OH more effectively than an equal volume of water. An example of a common buffer is a solution of acetic acid CH 3 COOH and sodium acetate.
Buffer in chemistry solution usually containing an acid and a base or a salt that tends to maintain a constant hydrogen ion concentration. Buffer capacity is the amount of acid or base that can be added before the pH of a buffer changes. In other words a buffer is a solution that is able to maintain the pH condition of a solution.
Buffer Solution Definition Biology A buffer solution more precisely pH buffer or hydrogen ion buffer is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base or vice versaIts pH changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it. They resist a change in pH upon dilution or upon the addition of small amounts of acidalkali to them. It resists the change in pH upon dilution or addition of a small amount of an acid or a base to the solution.
DEFINITION A buffer is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid its salt or a weak base its salt that resist a change in pH on the addition of either acid or base. Buffer solution Definition A buffer solution is an aqueous solution that consists of a mixture of a weak acid and a conjugate base of a weak acid or vice versa. 1 chemistry A buffer solution.
A buffering agent is a weak acid or weak base that helps maintain the pH of an aqueous solution after adding another acid or base. Most buffers consist of a weak acid and a weak base. A buffer is an aqueous solution that has a highly stable pH.
If you add an acid or a base to a buffered solution its pH will not change significantly. A lot of biological and chemical reactions need a constant pH for the reaction to proceed. It is the main buffer in blood plasma and consists of bicarbonate HCO 3 and carbonic acid H 2 CO 3.
A buffer solution is a solution containing weak acids and their conjugate bases or weak bases and conjugated acids that are resistant to pH changes. An example of a buffer solution is bicarbonate in blood which maintains the bodys internal pH. This solution is quite important in the field of chemistry.
Buffer Solution is a water solvent based solution which consists of a mixture containing a weak acid and the conjugate base of the weak acid or a weak base and the conjugate acid of the weak base. Its pH changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it. This does not mean that the pH of buffers does not change.
Buffers typically consist of an acid-base pair with the acid and base differing by the presence or absence of a proton a conjugate acid-base pair. Note- A lot of biological chemical reactions need a constant pH for the reaction to proceed. The protection is afforded by the presence in the solution of a weak acid and related salt for example acetic acid and sodium acetate which maintains the equilibrium by means of ion transfer and neutralization.
Buffers are extremely useful in these systems to maintain the pH at a constant value. A buffer solution refers to an aqueous solution. It is a water-based salt solution containing disodium hydrogen phosphate sodium chloride and in some formulations potassium chloride and potassium dihydrogen phosphate.
A biological buffer is an organic substance that has a neutralizing effect on hydrogen ions. An acid-base balancing or control reaction by which the pH of a solution is protected from major change when acid or base is added to it. A buffer is an aqueous solution used to keep the pH of a solution nearly constant.
Buffer solutions are used as a means of keeping pH at a nearly constant value in a wide variety of chemical applications. The bicarbonate buffer neutralizes stronger dietary and metabolic acids HA converting them into weak bases A with the increase in H 2 CO 3. A buffer consists of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid.
For instance one of the buffers that maintain the pH of human blood involves carbonic acid H.
 Trick To Find The Ph Of A Buffer Solution Class 11 Chemical Equilibrium Youtube In 2020 Buffer Solution Solutions Chemical
Trick To Find The Ph Of A Buffer Solution Class 11 Chemical Equilibrium Youtube In 2020 Buffer Solution Solutions Chemical
 A Buffered Vs A Non Buffered Solution Chem13 News Magazine University Of Waterloo
A Buffered Vs A Non Buffered Solution Chem13 News Magazine University Of Waterloo
 Buffers Definition Overview Expii
Buffers Definition Overview Expii
 Buffer Solution Preparation Of Buffer Solution Acidic Basic Buffer Buffer Action Buffer Solution Electron Configuration Solutions
Buffer Solution Preparation Of Buffer Solution Acidic Basic Buffer Buffer Action Buffer Solution Electron Configuration Solutions
 Common Ion Effect Buffer Solution And Solubility Product Buffer Solution Solubility Solutions
Common Ion Effect Buffer Solution And Solubility Product Buffer Solution Solubility Solutions
 Bicarbonate Buffer System Example Of Multiple Equilibria Teaching Chemistry Medical School Studying Biochemistry
Bicarbonate Buffer System Example Of Multiple Equilibria Teaching Chemistry Medical School Studying Biochemistry
 Buffer Solutions Biochemistry The Biology Notes
Buffer Solutions Biochemistry The Biology Notes
 Buffer Buffering Capacity Properties Of Good Buffer And Role Of Buffer In Vitro And In Vivo Online Biology Notes
Buffer Buffering Capacity Properties Of Good Buffer And Role Of Buffer In Vitro And In Vivo Online Biology Notes
 A A Diagram Of The Process Of Agarose Gel Electrophoresis 1 An Agarose And Buffer Solution Is Heated And Poured Microbiology Study Chemistry Study Biology
A A Diagram Of The Process Of Agarose Gel Electrophoresis 1 An Agarose And Buffer Solution Is Heated And Poured Microbiology Study Chemistry Study Biology
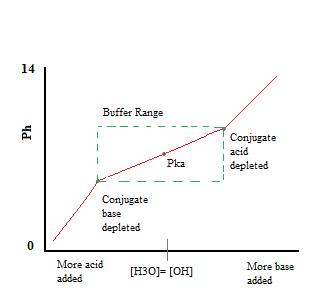 Introduction To Buffers Chemistry Libretexts
Introduction To Buffers Chemistry Libretexts
 What Is A Buffer And How Does It Work Westlab
What Is A Buffer And How Does It Work Westlab
 Buffer Solution Acidic Buffer Basic Buffer Animation Buffer Solution Electron Configuration Solutions
Buffer Solution Acidic Buffer Basic Buffer Animation Buffer Solution Electron Configuration Solutions
 Buffer Solutions Definition Types Preparation Examples And Videos
Buffer Solutions Definition Types Preparation Examples And Videos
 Buffer Solution Its Characteristics Types And Preparations
Buffer Solution Its Characteristics Types And Preparations